Gingivitis: causes, signs, harms and effective treatment
Gingivitis is a fairly common disease, easily recognized by the swelling of the gums and pain emanating from the gums and teeth. The same article below learns in detail about gingivitis of the teeth to handle it promptly, avoiding dangerous complications.
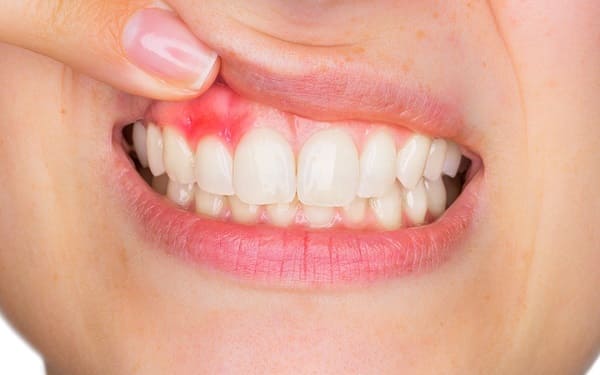
1. What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a condition in which the gums are red and swollen, the long-term plaque at the gum line is irritated and easy to cause bleeding gums. Without timely treatment and improved oral care, gingivitis will quickly turn bad into periodontitis, even tooth loss.
2. Signs of gingivitis
- Swollen gums: swollen gums that are redder than usual, puffy or tender, may be accompanied by pain
- Teeth bleed easily when brushing, flossing or eating hard foods.
- When you have gingivitis, the color of your gums will change from rosy to deep red, dark red, dark red brown. At this time, my gums hurt.
- Breath has a fouler smell than usual due to the bacteria residing in the gum tissue for a long time that is not cleaned
- Longer teeth: swollen gums cause gums to shrink, receding gums make teeth look longer
- Gingivitis causes teeth to lean forward or backward, increasing the space between teeth
- Teeth become more sensitive, loose and prone to decay
- Feeling uncomfortable, edema
- Spontaneous bleeding in severe gingivitis
- Accompanying symptoms: loss of appetite, insomnia, sudden fever, etc.
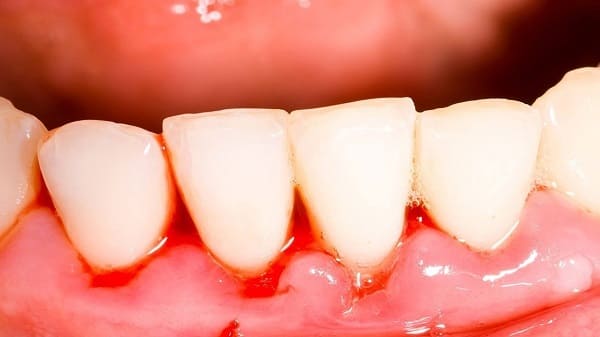
3. Causes of swollen gums
- Poor or improper oral hygiene. Plaque, bacteria accumulate for a long time into tartar, creating favorable conditions for the arising of swollen gums.
- Smoking cigarettes regularly
- Pregnant women, after giving birth or coming to the menstrual cycle, are susceptible to bacteria attack when there are hormonal changes and weaker resistance than usual.
- Some diseases such as diabetes, leukemia, HIV … weakening the immune system also contribute to the development of gingivitis.
- Some drugs such as antihistamines, antidepressants, … reduce the amount of saliva secreted, the body does not clean all bacteria on its own, on the contrary, creates conditions for them to grow.
- Teething wisdom teeth swollen gums and pain.
- Bad effects from other oral diseases such as tooth decay, tooth abscess, etc.
4. How to prevent gingivitis
- Clean your teeth every 2 days, or 30 minutes after meals. Remember to brush your teeth gently, brush all sides and take enough time from 2 to 3 minutes.
- Use dental floss, water flosser to clean between teeth at least once a day.
- Cure gingivitis by remembering to take regular tartar.
- Ask your dentist for advice on how to improve your oral care.
- Quit smoking, tobacco to maintain oral hygiene, and prevent bad breath.
- Drink enough water every day, limit dry mouth.
- Add foods that are good for your teeth, such as vegetables and fruits, foods rich in vitamins, especially vitamin A and vitamin C.
- Perform gum massage every day to relieve pain and increase blood circulation to the gum area for more effective healing.

As can be seen, the prevention of gingivitis is simple and easy just by following the correct oral care regimen. One of the friendliest and most soothing ways to reduce the risk of this condition is to use a salt water mouthwash to eliminate bacteria. Dr.Muoi is one of the reputable brands recommended by dentists.

You Can Refer To More Articles:
Should I wash my nose with physiological saline?
Instructions for Self-healing Sinusitis with Physiological Salt Water
Tips for Treating Allergic Rhinitis with Physiological Salt Water Simple and Effective
Instructions on how to hydrate with salt water to treat bad breath
